Hip arthrosis (coxarthrosis) is a chronic, gradual progressive disease, in the absence of timely and proper treatment, can lead to complete loss of movement in it.The end suggests that it is not inflammatory, but a degenerative process prevails.
The symptoms of this disease vary depending on the stage.At the outset, this is hardly noticeable discomfort that occurs when walking and exercise.Perhaps the manifestation in the form of mild pain in the thigh that passes at rest.In this case, the pain can be felt not only in the thigh but also in the groin or in the knee.
As a rule, coxarthrosis is a process that has leaked for many years, characterized by a gradual change in cartilage, followed by bone deformity and loss of joint functionality.Most of all, it affects people after 40 years, but many young patients are also found.
Reasons
Why does hip arthrosis occur and what is it?The causes of coxarthrosis may be different, but the picture of the disease is always the same.It all starts with changes in the articular cartilage, which is smoother and loses the property of depreciation of loads.The body compensates for the stratification of cartilage tissue by the formation of bone growths along the edge of the joint surfaces, leading to deformation of the joints and bones of varying degrees.
The main causes of this joint disease:
- InjuriesSThis reason may not be a large lesion, but in many cases chronic microtraumas affect the development of the disease, which contributes to cracking and thinning of cartilage.They also affect the grief of the joint capsule, which causes a lot of damage to accumulate.Often recurrent micro -traumas are the precursor to the onset of such a disease.
- Excessive loadsWhich leads to systematic micro -trauma as well as joint injuries.Most often, this is found in people involved in heavy physical labor or professional athletes.In this case, treatment without changing lifestyle limitations or loading is also ineffective and is often accompanied by relapses.
- Hereditary predispositionSThis includes anomalies in the development of the femur itself, the underdevelopment of the joint elements, etc.In this case, the so -called dysplastic arthrosis of the hip joint occurs.
- IllnessSFor example, arthritis in the absence of proper treatment may degenerate into arthrosis over time.This is due to the fact that during arthritis the properties of cartilage change of tissues, blood circulation occurs.This gradually leads to the development of a degenerative process.
- Excess body weightSExcess body weight, even when walking, there is a load on the joints exceeding their physiological limits of power.
Depending on the cause of the disease and its pathogenesis, 2 main types of arthrosis of the hip joint are distinguished.
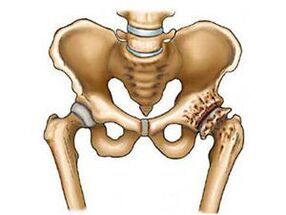
- CoxarthrosisSIn this case, the disease develops very slowly and begins with impaired tissue blood supply.The reasons for the development of this type of arthrosis are rooted in violation of metabolism, which is more characteristic of people over 50 years of age.Primary arthrosis of the hip joint is the most often diagnosed.
- Secondary coxarthrosisSIn this case, the disease develops against the background of the systemic inflammatory lesion of many joints in the body.Inflammation can be both infectious and autoimmune.
In the initial stage of coxarthrosis, only mild pain or discomfort in the joint is worried.Often such signs are ignored, resulting in the disease progressing.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint, whose symptoms cannot be ignored, can have serious consequences.There are several main signs of the disease that depend on the stage of the disease:
- Joint pain is the most obvious symptom by which any TBS disease can be taken.The intensity and nature of the sensations usually depends on the scene.
- Restricting limb mobility is also a symptom of coxarthrosis.For the early stage, the feeling of "restriction" of the joint, which passes after some load, is characteristic.
- The weakening of the muscles of the hip joint can now be observed in the second stage of the disease, reaching the third to complete atrophy.
- Changing the length of the leg due to the deformation of the pelvis is characteristic of "neglect" osteoarthritis.
- Main or changing gait is a very likely sign of bone deformity.
- An excellent joint crisis is not always a sign of arthrosis.They are usually taken into account if there are other symptoms.
The main characteristic of coxarthrosis is the pain, the nature of which, duration, location and intensity, depend on the stage of the disease.
Hip arthrosis becomes a first degree
This stage of the disease is characterized by pain in the joint and thigh, sometimes in the knee, which occurs after physical activity and disappears after rest.The mobility of the joint is not limited and there are no violations of the gait.
First degree coxarthrosis is the initial stage of the disease, starting treatment that you can still stop the process of destruction and deformation of the joint and maintain its functions completely.But, unfortunately, many do not consider it necessary to see a doctor because of poor joint pain, and the disease in the meantime progresses.
Hip arthrosis joint 2 degrees
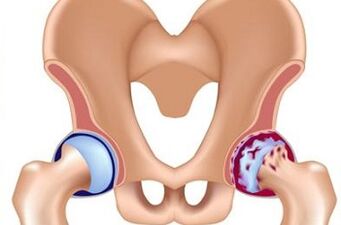
It manifests itself more clearly - the intensity of the pain grows, it happens not only after the load, but also at rest, there is a limit to the motor functions.In particular, coxarthrosis is characterized by difficulty in performing the projection (rotation of the thigh inwards) and abduction, a contracture is formed.
In X -ray study, we see a narrowing of the joint space and the appearance of bone growth surfaces.The rotating cavity and femur are deformed.The muscles of the thigh on the side of the lesion begin to atrophy, and the pain syndrome spreads from below, capturing both the knee joint and the inguinal area (it is important to understand that this will not be accompanied by dystrophic changes in the knee joint).
Hip arthrosis becomes 3 degrees
The signs of the disease are expressed and constant.The pain syndrome is ahead of the night.When walking, the patient uses the support.The muscles of the lower legs and thighs are gradually atrophy, and the sick leg of the sick person becomes much short.
Often, up to the 3rd degree, the joint gap completely disappears and the joints grow together in a bone structure, this demonstrates a picture.As a result, complete immobility of the joint occurs.
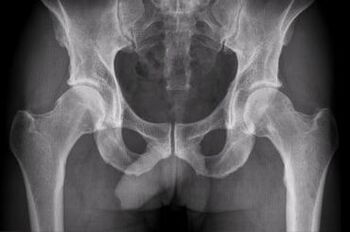
Radiographs determine extensive bone growths on the side of the roof of the rotating and head of the femur, a sharp narrowing of the gap of the joints.The femur neck is significantly expanded and shortened.
Diagnostics
Before you understand how to treat hip arthrosis, it is necessary to make a diagnosis properly.In the case of suspicion of coxarthrosis, a person will be directed to a biochemical blood test - in the presence of the disease patients have a slight increase in ESR, globulins, immunoglobulins and serumoid.
The next stage of the detection of arthrosis is a photo with X -Ray.Will identify:
- A cartilage guide,
- Bone growths on the border of cartilage,
- narrowing the distance between the joints,
- Bone tissue compaction under the cartilage.
Unfortunately, the X -ray photo does not allow the capsule of the joint and the cartilage itself if you need to get information about these soft tissues, then the patient will be directed to tomography.
Treatment of hip arthrosis joint
With diagnosed arthrosis of the hip joint, treatment will depend directly on the stage at which the disease is located.The general treatment regimen provides for the following goals:
- elimination of pain and discomfort in the area of the inflamed joint;
- to establish the nutrition of the intra -shaped cartilage and to begin the process of its recovery;
- Eliminate the deficiency of intra -articular fluid;
- Activation of microcirculation in joint tissues;
- Eliminate the increased load of the hip joint;
- strengthening the muscles that surround, protect and maintain joints;
- Prevention of deformity and increase mobility in the thigh joint.
All this can only be achieved with the help of an integrated approach, which should include not only drug therapy but also a change in lifestyle to get rid of risk factors of coxarthrosis.
- In the third stage of the disease, treatment involves surgery during which the joint is replaced by an endoprosthesis, while part of the prosthesis is closed in the femur and is part of the pelvis.The surgery is quite complicated, a long time and requires a long rehabilitation period.
- With I and II degree of arthrosis of the hip joint, treatment without surgery is performed.Used: non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, vasodilating drugs, hormonal steroid drugs, local medicines -mellion, lotions, compresses.
All these medicines are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.Some of them are effective in the form of injections directly to the affected joint area.Such injections can only be performed by qualified medical staff.Therefore, self -measurement is not strictly recommended.
Methods without medicine
In addition to the use of medicines, doctors recommend non -disruption methods to combat the disease.These include the following methods of treating this disease:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- Joint breeding;
- diet.
Physiotherapy used for arthrosis includes the following types of treatment:
- magnetotherapy;
- UHF and ultrasound therapy;
- aero and electrotherapy;
- inductothermia;
- phototherapy;
- The use of laser technology.
All these methods can only be used to improve blood supply to the joints and relieve spasms.
Drug therapy
The combined treatment of hip arthrosis envisages the appointment of the following drug groups:

- Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs, they all eliminate the pain, relieve inflammatory processes, but do not restore cartilage tissues.
- ChondroprotectorsSCartilage tissue nutrition preparations.Accelerate its recovery.Important in 1.2 phase of treatment of arthrosis.With 3 degrees, cartilage disease has already been destroyed, these drugs will be useless.You should take drugs for a long time, take several courses.
- MonsolelaxantsEliminate muscle cramps in the area of inflamed joints, contribute to improving the blood supply to the tissues.
- Ointments and creamsSTherapeutic ointments are to alleviate the condition of a sick person, but do not contribute to full recovery.Warming ointments are very suitable.They irritate the receptors of the skin and therefore reduce pain syndrome.Warming ointments also work to restore increased blood circulation in the tissues and muscles located around the patient.
- Steroid injections into the joint cavity, Injections of these drugs are prescribed to relieve the exacerbation of the disease and eliminate severe pain.
- Vasodilative drugs, expand the vessels inside the joint cavity and close to it, thus improving the supply of the nutrients needed to repair tissues.
It is not necessary to rely on folk remedies for treatment.But some healers recommend a tincture of lemon, garlic or celery root for the treatment of joints and bones.
Massage in the treatment of coxarthrosis
With the deformation of hip arthrosis, massage treatment produces good results.Coxarthrosis massage is a very effective and useful method.It is desirable to do the massage by a good specialist and as often as possible.
Its effect is aimed at improving blood circulation, strengthening the muscles, eliminating painful spasm, swelling and muscle tension, as well as an increase in diastasis between the articulations of the joint.
In the absence of a professional massage therapist, a massage can be done.Massage with arthrosis can be performed both manually and with the help of various massage devices and even water jets (hydrocynesiotherapy).
Gymnastics
The treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint with physical education lies in achieving two tasks: to increase leg mobility and prevent muscle atrophy.All standard LFK complexes for coxarthrosis also have a common strengthening nature and positive effect on the whole body.
The gymnastic exercise complex is prescribed by a specialist.The first couple of medical physical education should be conducted under the supervision of a doctor.He will show how to properly perform any movement and also control the proper load of the hip joints.
Diet
Basic recommendations:
- Preference for porridge on the water.
- Use enough animal protein: fish (except for salty), homemade meat, beef.
- Use at least 5 servings of vegetables a day (one serving - 100 grams, can be used as a garnish).
- Mandatory dairy products: cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented.
- Exclude alcohol, coffee, strong black tea.
- Turn off sweet, flour.
- Eat a little, but often.
The diet will reduce the load on the hip joints and provide them with everything you need to repair the tissues.


















